In the connection between steel structures and concrete foundations, foundation anchor bolts play a decisive role in ensuring overall structural safety. Among them, J shaped anchor bolts are widely used due to their distinctive hooked end design, which provides enhanced anchorage performance.However, selecting the right J bolt for concrete is not as simple as it may seem. An inappropriate choice can compromise safety or lead to unnecessary costs. This article provides a clear and practical guide to selecting J bolts for concrete applications to ensure both structural reliability and economic efficiency.
1. What Are J-Shaped Foundation Bolts?
J-shaped anchor bolts are a type of cast in place foundation bolt characterized by a 180 degree hooked end embedded in concrete. This hook significantly improves the mechanical interlock between the bolt and the concrete, enhancing bonding strength and pull out resistance. Compared with other anchor bolt types such as L-shaped, claw type, or double-ended bolts,J bolts feature a simple structure and straightforward manufacturing process. However, their load bearing capacity is relatively limited, making them most suitable for light to moderate structural loads.
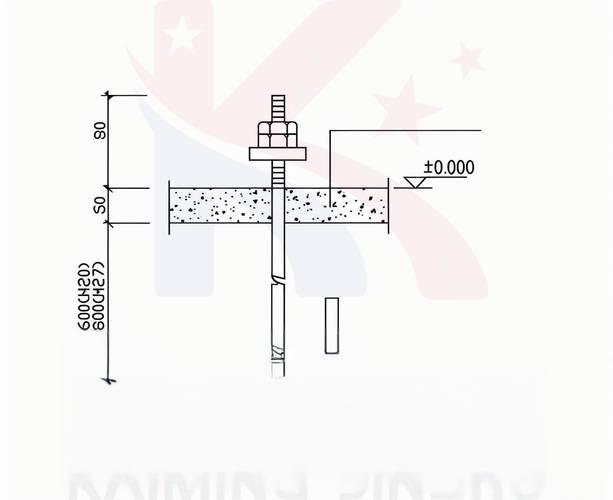
2. Typical Applications of J Bolts
2.1 Strength Grade Requirements
According to DL/T 1236-2021,Anchor Bolts and Nuts for Transmission Line Towers, J shaped anchor bolts are primarily recommended for Grade 4.6 applications. This aligns well with the mechanical characteristics of J bolts, as higher strength grades are unnecessary and often impractical for this bolt type.
2.2 Recommended Size Range
Due to manufacturing limitations and performance considerations, J bolts are generally recommended for sizes M36 and below. Larger diameters require heating during bending, which makes dimensional accuracy difficult to control and may negatively impact product quality.
2.3 Suitable Application Scenarios
J shaped anchor bolts are best suited for applications with relatively low load demands, including:
Foundations for small transmission towers
Light steel structures
Equipment bases with limited uplift forces
Projects in regions with low seismic requirements
3. Key Factors for Selecting J Bolts
3.1 Understanding Strength Grades
Anchor bolt strength grades (e.g., 4.6) convey essential mechanical properties:
The first number represents 1/100 of the tensile strength,The second number represents the yield ratio (yield strength ÷ tensile strength) ,For example, a Grade 4.6 bolt has:Tensile strength: 400 MPa and Yield strength: 240 MPa.
3.2 Material Selection
Although current standards classify anchor bolts by performance grade rather than material, J bolts are traditionally manufactured from Q235 carbon steel. This material offers excellent ductility and weldability, making it well suited for bending and forming operations.
3.3 Embedment Length Requirements
Proper embedment depth is essential to prevent pull out failure and ensure reliable anchorage performance. In general, the minimum embedment depth for J shape anchor bolts should be 20–25 times the bolt diameter, depending on load conditions and concrete strength. For C20 concrete, an embedment depth of 20 times the bolt diameter is commonly adopted in practice. In addition, the hooked end should have a minimum hook length of 120 mm to provide sufficient mechanical interlock with the concrete.

4. Design Calculation Principles
Anchor bolt design must satisfy the following condition:
Number of bolts × Effective cross-sectional area × Design tensile strength > Uplift force
Example Calculation
Given:
-
Uplift force: 1400 kN
-
Bolt type: Grade 4.6 M64
-
Net cross-sectional area: 2676 mm²
-
Design tensile strength: 160 N/mm²
Required number of bolts:
1400 kN ÷ (2676 mm² × 160 N/mm²) ≈ 3.27
After rounding up, 4 anchor bolts are required to meet the design demand.
5. Installation Best Practices
5.1 Accuracy Control During Installation
Bolt position, elevation, and exposed length must comply with drawings.Positioning templates should be used; hole diameters should be 2 mm larger than the bolt diameter.Bolts must be securely fixed before concrete pouring to prevent movement
5.2 Corrosion Protection
Proper corrosion protection is essential, especially in aggressive environments. Common methods include Hot-dip galvanizing and Anti-corrosion coatings or paints
5.3 Important Precautions
Avoid using welded anchor bolts in environments below –30°C
High strength bolts (Grade 8.8 and above) should not be welded.
The hook orientation should enhance pull-out resistance and must not interfere with reinforcement bars.
6. Common Issues and Practical Solutions
6.1 Elevation Deviation Corrections
Excess height: Cut off surplus length and re-thread
Minor shortage (<15 mm): Heat with an oxy-acetylene torch and stretch
Major shortage (>15 mm): Excavate around the bolt, cut it 100 mm above the pit bottom, and weld a new bolt section
6.2 Avoiding Common Selection Mistakes
Do not over specify strength: Grade 4.6 is sufficient for most J bolt applications
Consider low temperature effects, such as steel “blue brittleness”
Avoid oversized bolts, as J bolts larger than M36 are difficult to manufacture and control accurately
7. Trends in Standards and Specifications
According to DL/T 5486-2020 ,Technical Code for Design of Overhead Transmission Line Towers, anchor bolt selection has shifted from material-based classification to performance grade based selection. This change emphasizes actual mechanical behavior and improves consistency in quality control.
Within the same project, it is recommended to standardize anchor bolt sizes and strength grades to simplify construction, inspection, and inventory management.
Conclusion
Selecting the right J bolts for concrete requires a balanced evaluation of structural load, environmental conditions, construction practices, and cost efficiency. By understanding the strengths and limitations of J bolts and following current standards, engineers can ensure both safety and reliability. Foundation anchor bolts seems small, but they are fundamental to structural integrity. When load demands are moderate and bolt sizes are M36 or smaller, J anchor bolts remain a practical and economical solution thanks to their simple design and proven performance.





